The donuts code & the math behind
The Donuts Code
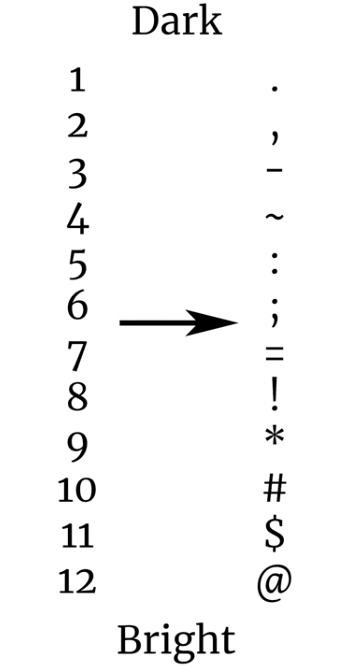
The spinning "donuts" that has brought some attention recently and was created by the amazing Andy Sloane. No wonder, a flying donut on your terminal? You can find the code below in c. The "pixels" are ASCII characters .,-~:;=!*#$@ that accounts for the illumination value of the surface, but I'll explain step by step below along with the math.
Mission: 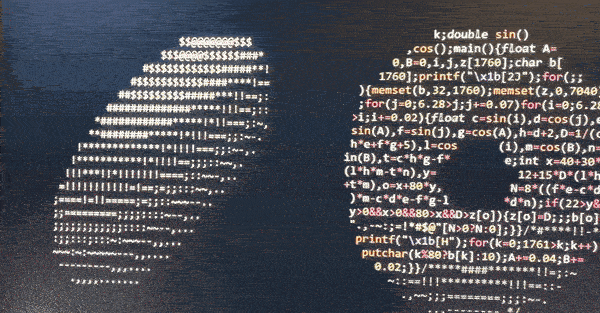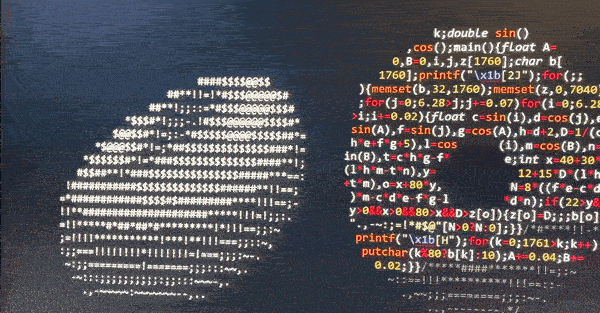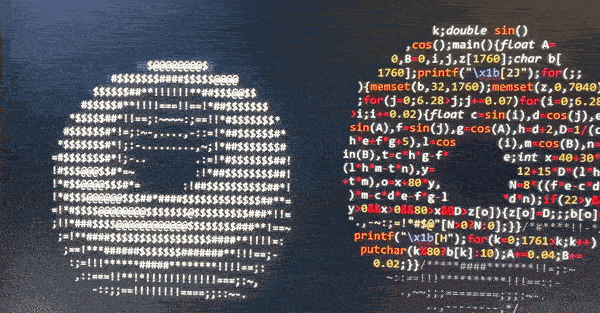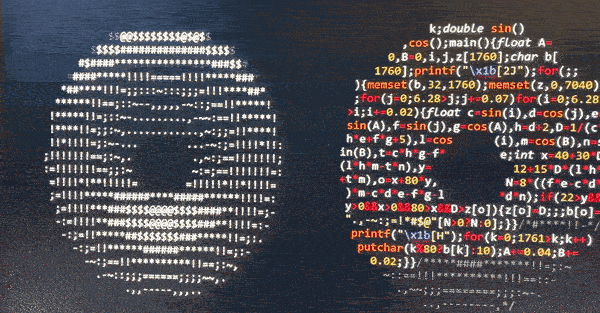
Steps
Create a circle of radius R2 centred at R2
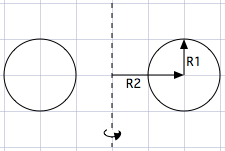
Create a torus('donuts') which rotates on the Y axis
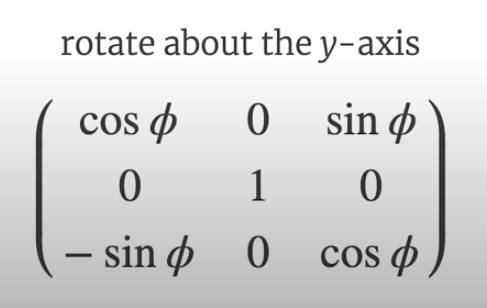
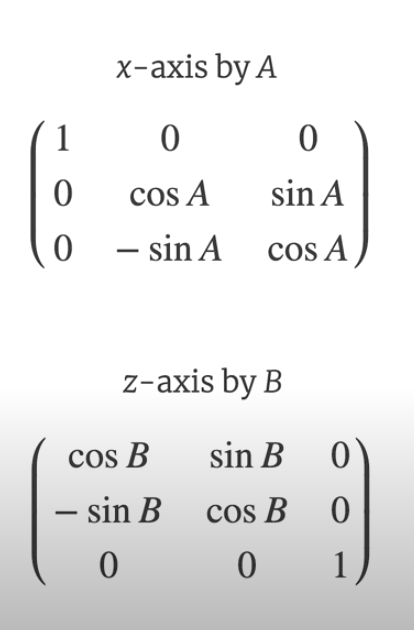
Now, we need to rotate about the X and Z axis so it looks like it's floating and spinning on the screen. Basically, a flying donut. Why not?
Well, how to map this 3D objet into 2D ie terminal screen?
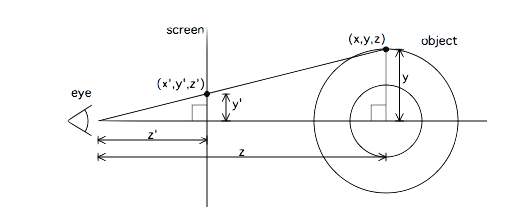
Each character in the code corresponds to a pixel on our terminal. However, how to shade it? For this, we calculate the dot product of the surface normal and the direction of the light. This will say how light and how dark will look on the screen.
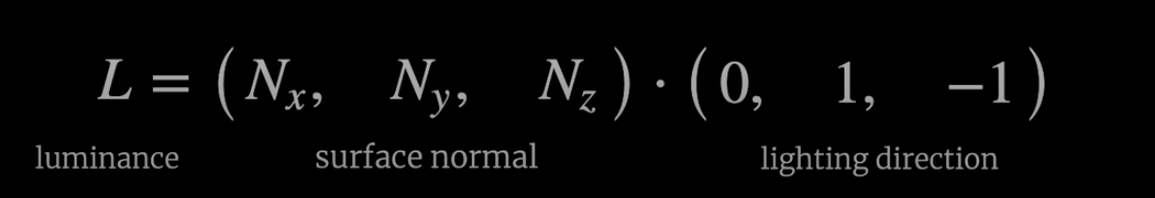
The output of the dot product will be: 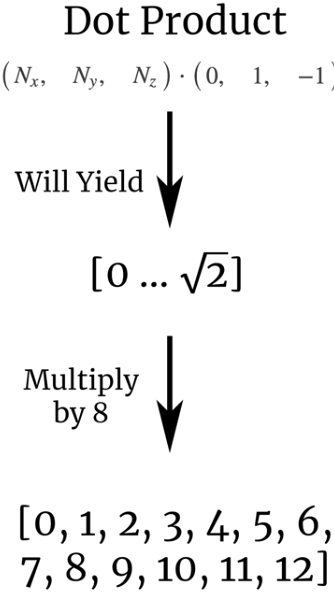
- Finally you map the result of the dot product (step 4) to these characters to tweak the lighting. That's it!

Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
float A = 0, B = 0;
float i, j;
int k;
float z[1760];
char b[1760];
printf("\x1b[2J");
for(;;) {
memset(b,32,1760);
memset(z,0,7040);
for(j=0; j < 6.28; j += 0.07) {
for(i=0; i < 6.28; i += 0.02) {
float c = sin(i);
float d = cos(j);
float e = sin(A);
float f = sin(j);
float g = cos(A);
float h = d + 2;
float D = 1 / (c * h * e + f * g + 5);
float l = cos(i);
float m = cos(B);
float n = sin(B);
float t = c * h * g - f * e;
int x = 40 + 30 * D * (l * h * m - t * n);
int y= 12 + 15 * D * (l * h * n + t * m);
int o = x + 80 * y;
int N = 8 * ((f * e - c * d * g) * m - c * d * e - f * g - l * d * n);
if(22 > y && y > 0 && x > 0 && 80 > x && D > z[o]) {
z[o] = D;
b[o] = ".,-~:;=!*#$@"[N > 0 ? N : 0];
}
}
}
printf("\x1b[H");
for(k = 0; k < 1761; k++) {
putchar(k % 80 ? b[k] : 10);
A += 0.00004;
B += 0.00002;
}
usleep(30000);
}
return 0;
}
Credits
Check out Andy Sloane blog post for more details about the math: Blog Post: "Donut math: how donut.c works" blog post by Andy Sloane
Checkout Alex Friedman for a quick explanation and code: Donut-shaped C code that generates a 3D spinning donut